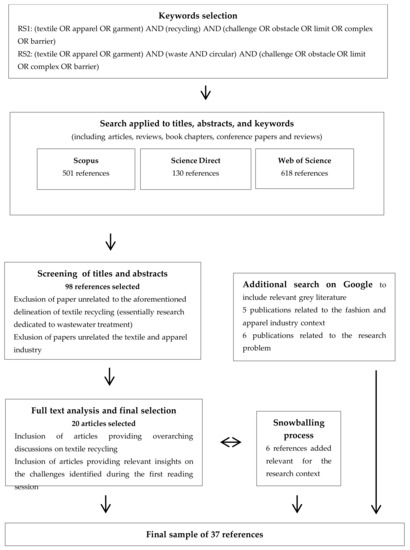
Textile recycling challenges in Bangladesh include inefficient waste management systems and lack of awareness about the benefits of recycling. Bangladesh faces obstacles in effectively managing textile waste due to inadequate infrastructure and limited resources, as well as a lack of education and awareness among the public and industry stakeholders.
These challenges hinder the implementation of effective recycling practices and contribute to environmental pollution and resource depletion. However, with concerted efforts to improve waste management infrastructure and promote awareness about textile recycling, Bangladesh can overcome these challenges and move towards a more sustainable textile industry.
By adopting innovative recycling technologies and promoting circular economy principles, Bangladesh can significantly reduce textile waste and create a more environmentally friendly and economically viable industry.
Textile Recycling Challenges In Bangladesh
Textile recycling is an essential process that enables the reuse of old textiles into new products, reducing waste and the environmental impact of textile production. Bangladesh, being one of the largest textile producers globally, faces several challenges in achieving an efficient and sustainable textile recycling system. These challenges include limited awareness and education, as well as infrastructure and technology constraints.
Limited Awareness And Education
In Bangladesh, limited awareness and education about textile recycling contribute to the challenges faced by the industry. Many people are unaware of the benefits of recycling textiles or how to properly dispose of their unwanted clothing. This lack of awareness leads to a low level of participation in textile recycling programs, hindering the growth of a sustainable recycling ecosystem.
Moreover, the lack of education means that individuals and organizations often fail to recognize the importance of segregating textile waste from other types of refuse. Without separation at the source, the process of recycling becomes more difficult and less efficient, as different types of waste need to be sorted by hand.
Infrastructure And Technology Constraints
In addition to limited awareness and education, Bangladesh also faces significant infrastructure and technology constraints when it comes to textile recycling. The country lacks well-established recycling facilities and collection systems to handle the volume of textile waste generated.
Moreover, the recycling technology available in the country is often outdated and insufficient to process the vast amounts of textile waste produced. The lack of appropriate machinery and equipment hinders the efficient processing and transformation of used textiles into new, usable materials.
The inadequate infrastructure also extends to the transportation and logistics aspect of textile recycling. Limited transportation networks and inadequate storage facilities make it difficult to collect and transport textile waste from various sources to recycling centers.
Environmental Impact Of Textile Waste
The environmental impact of textile waste in Bangladesh poses significant challenges for textile recycling. With the country's booming garment industry, the disposal of textile waste has become a pressing issue. Efforts towards sustainable textile recycling face hurdles due to inadequate infrastructure and limited awareness, posing a challenge for effective waste management.
Pollution And Landfill Concerns
Textile waste is causing severe pollution and landfill concerns in Bangladesh. The rapid growth of the textile industry has led to an increase in the production and consumption of garments, which in turn has resulted in a high volume of textile waste. The disposal of this waste has become a significant challenge, with limited infrastructure and resources to handle the massive quantities of discarded textiles.Resource Depletion And Energy Consumption
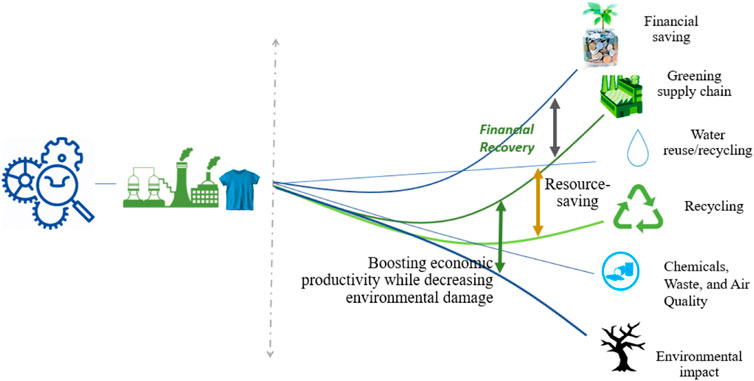
The textile industry in Bangladesh heavily relies on natural resources, such as water, land, and energy, for its production processes. However, the improper management of textile waste leads to the depletion of these valuable resources. For instance, the dyeing and finishing processes require a substantial amount of water, and when garments containing dyes and chemicals are discarded, they contaminate water sources, further exacerbating resource depletion. Notably, textile waste also contributes to energy consumption. The production of new textiles requires a significant amount of energy, including electricity and fossil fuels, leading to increased greenhouse gas emissions. By adopting sustainable practices and recycling textile waste, the consumption of energy in the textile industry can be reduced, contributing to the overall conservation of resources.Potential Solutions And The Role Of Recycling
Addressing the environmental impact of textile waste requires a multi-faceted approach. One key solution lies in the adoption of textile recycling methods. Textile recycling not only reduces the pollution and landfill concerns associated with textile waste but also offers various other benefits. Recycling textiles can help minimize pollution by diverting these materials from landfills, where they would otherwise degrade and release harmful chemicals and greenhouse gases. Instead, recycling allows these materials to be repurposed, reducing the need for additional resource extraction and minimizing energy consumption. Moreover, textile recycling can lead to the recovery of valuable materials and resources. By reusing fibers from discarded garments, new textiles can be produced, decreasing the demand for virgin materials. This process helps conserve natural resources while also reducing energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions. Overall, addressing the environmental impact of textile waste requires a shift towards sustainable practices and effective textile recycling systems. By doing so, Bangladesh can mitigate pollution and landfill concerns, conserve natural resources, and promote a more environmentally friendly textile industry.Social And Economic Implications
Bangladesh faces several social and economic implications due to challenges in textile recycling. These implications have a significant impact on the country's employment opportunities, community health, and livelihoods of the people. Let's explore the key ramifications in detail:
Employment Opportunities
The textile recycling challenges in Bangladesh have disrupted job opportunities in the sector. This has led to a decline in employment and undermined the livelihoods of many individuals who depend on the textile industry for income.
Community Health And Livelihood
The inadequate management of textile waste has direct implications on community health and livelihoods in Bangladesh. Improper disposal methods contribute to environmental pollution, posing risks to the well-being of local residents and affecting their ability to sustain a healthy lifestyle.
Credit: www.mdpi.com
Government Policies And Initiatives
Bangladesh faces significant challenges in textile recycling due to inadequate government policies and initiatives. The lack of proper regulations and incentives hampers the effective management of textile waste, hindering sustainable and eco-friendly practices. Finding feasible solutions to address these challenges is crucial for the country's environmental goals.
Regulatory Framework
Bangladesh, being one of the largest textile producers worldwide, faces numerous challenges in textile recycling. The government has implemented various policies and initiatives to address these challenges and promote sustainable textile recycling practices. The regulatory framework is the cornerstone of these efforts. To regulate the textile recycling industry effectively, the government has established strict guidelines and standards. These regulations ensure that textile recycling operations adhere to environmental, health, and safety standards. Companies involved in textile recycling must obtain licenses and permits to operate legally. This ensures that only responsible and qualified entities are engaged in this sector.Incentives And Support Programs
The government of Bangladesh understands the importance of encouraging textile recycling and provides various incentives and support programs to facilitate the growth of this industry. These initiatives aim to attract more businesses and individuals to participate in textile recycling and contribute to a greener and more sustainable future. One major incentive offered by the government is financial support in the form of grants and subsidies. These incentives help offset the initial costs of setting up textile recycling facilities and encourage investment in advanced recycling technologies. Government support also includes tax incentives and exemptions, making it more economically feasible for businesses to engage in textile recycling. Moreover, the government has implemented programs to raise awareness about the benefits of textile recycling and educate the public on proper recycling practices. Through workshops, seminars, and public campaigns, they encourage consumers to recycle textiles instead of disposing of them in landfills. Additionally, the government collaborates with textile manufacturers and trade associations to develop sustainable and eco-friendly manufacturing practices. By promoting the use of recycled textiles and incorporating them into national procurement policies, the government creates a demand for recycled materials, further stimulating the growth of the textile recycling industry. In conclusion, the government of Bangladesh has taken significant steps to overcome the challenges faced in textile recycling. Through a comprehensive regulatory framework, incentives, and support programs, they are fostering a sustainable environment for textile recycling to thrive. These initiatives pave the way for a greener future and contribute to the overall development of the textile industry in Bangladesh.Collaborative Solutions And Partnerships
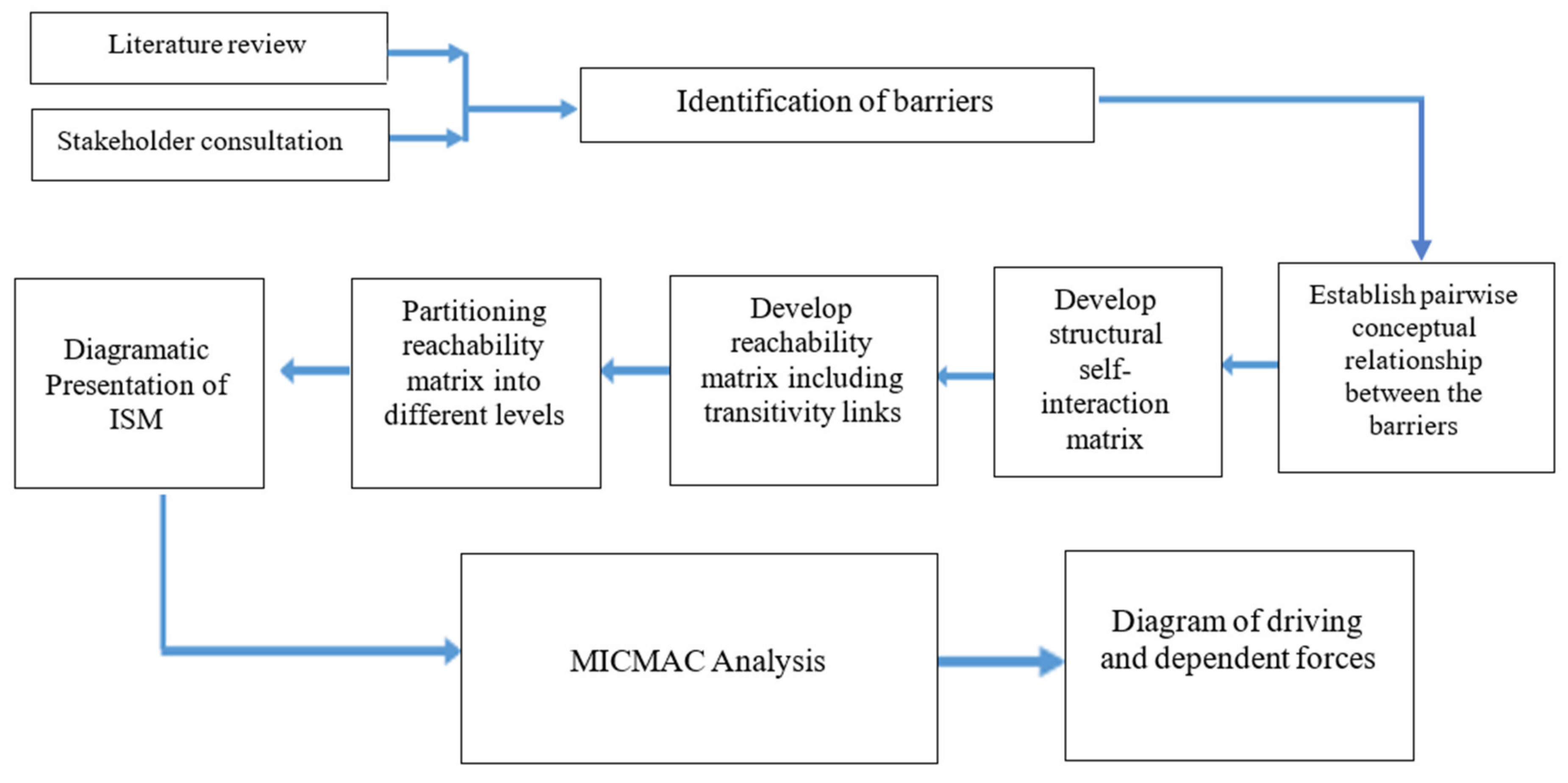
The challenges of textile recycling in Bangladesh are complex and require collaborative solutions to be effectively addressed. By engaging industry stakeholders and fostering cross-sector collaboration, we can overcome these obstacles and pave the way for a more sustainable textile recycling ecosystem.
Industry Stakeholder Engagement
Engaging industry stakeholders is crucial in creating a sustainable textile recycling system in Bangladesh. Companies involved in textile production, waste management, and recycling need to come together to find innovative solutions. By initiating dialogue and building partnerships, we can share knowledge and resources to develop effective strategies.
One way to engage industry stakeholders is by organizing forums and conferences where experts and practitioners can discuss challenges and share best practices. Such events allow stakeholders to learn from each other's experiences and find common ground for collaboration.
Cross-sector Collaboration
Cross-sector collaboration is another key aspect of addressing textile recycling challenges in Bangladesh. By bringing together government agencies, nonprofit organizations, and private enterprises, we can pool our resources and expertise to find sustainable solutions.
A collaborative effort can involve designing and implementing recycling initiatives that involve multiple sectors. For example, textile manufacturers can work hand in hand with waste management companies to establish efficient collection and sorting systems. Additionally, close collaboration with local communities can raise awareness about textile recycling and encourage participation.
Government support is also crucial in promoting cross-sector collaboration. By providing incentives and regulatory frameworks, authorities can encourage businesses to participate actively in recycling efforts. Governments can also play a pivotal role in facilitating partnerships between different sectors through policy initiatives and funding support.
In conclusion, tackling textile recycling challenges in Bangladesh requires collaborative solutions and partnerships. Through industry stakeholder engagement and cross-sector collaboration, we can overcome obstacles and work towards a more sustainable future for the textile industry.
Credit: www.mdpi.com
Credit: www.frontiersin.org
Frequently Asked Questions Of Textile Recycling Challenges In Bangladesh
What Are The Major Challenges That Bangladesh Faces Regarding The Growing Demand For Textiles?
The major challenges faced by Bangladesh in meeting the growing demand for textiles are labor rights issues, environmental sustainability concerns, competition from other countries, and lack of technological advancements in the industry.
What Are The Main Problems With The Garment Industry In Bangladesh?
The garment industry in Bangladesh faces issues like low wages, poor working conditions, and lack of worker rights. Safety concerns and environmental impact are also major problems.
What Are The Challenges Of Recycling Clothes?
Recycling clothes faces challenges such as the lack of proper collection and sorting systems, the presence of non-recyclable synthetic fibers, and the difficulty in recycling mixed fabrics. Proper infrastructure and consumer awareness are necessary to address these challenges and promote sustainable clothing recycling.
What Are The Barriers In Textile Recycling Industry?
Textile recycling industry faces various barriers such as lack of awareness, inadequate collection infrastructure, high processing costs, and difficulty in separating different types of fabrics. These challenges hinder the growth of the industry and the effective recycling of textiles to reduce waste and promote sustainability.
Conclusion
Textile recycling in Bangladesh faces significant challenges. The lack of awareness and infrastructure creates barriers to sustainable practices. By understanding these issues, we can work towards solutions for a more environmentally conscious industry. It's crucial for stakeholders to collaborate and take action to address these pressing concerns.
Comments
Post a Comment