Textile waste recycling methods include mechanical, chemical, and thermal processes, each with the goal of converting waste textiles into reusable or repurposed materials. The textile industry, known for its high consumption and waste generation, has been exploring various methods to reduce environmental impact.
Textile waste recycling is an innovative solution that not only reduces landfill waste but also conserves resources and minimizes pollution. Through mechanical methods, such as shredding and carding, waste textiles are mechanically processed to produce recycled yarns and fabrics. Chemical methods, such as solvent and enzymatic treatments, break down the fibers to recover useful materials.
Thermal processes involve the use of heat to decompose or melt the textiles to extract fibers or generate energy. These methods exemplify sustainability efforts within the textile industry, contributing to a circular economy and a greener future.
The Textile Waste Problem
Textile waste is a growing problem around the world, with millions of tons of textiles being discarded and ending up in landfills each year. This textile waste problem not only poses environmental challenges but also has significant economic costs. In this blog post, we will explore the environmental impact of textile waste and the economic costs associated with it.
The Environmental Impact Of Textile Waste
Textile waste contributes to various environmental issues, including pollution and resource depletion. Here are some key ways in which textile waste impacts the environment:
- Landfill Burden: When textile waste is sent to landfills, it takes up valuable space and contributes to the growing waste problem. Landfills release harmful gases, such as methane, which contribute to climate change.
- Resource Depletion: The production of textiles requires significant amounts of resources, including water, energy, and raw materials. By discarding textiles prematurely, we are wasting these valuable resources and increasing our ecological footprint.
- Pollution: Many textiles are manufactured using synthetic fibers, which release microplastics into the environment when they break down. These microplastics can end up in water bodies and harm marine life. Chemical dyes and treatments used in the textile industry also contribute to water pollution.
Addressing the environmental impact of textile waste requires implementing effective recycling methods and promoting sustainable practices throughout the textile supply chain.
The Economic Costs Of Textile Waste
The economic costs associated with textile waste are significant and extend beyond the direct cost of discarded textiles. Here are some key economic implications:
- Loss of Potential Revenue: When textiles are discarded instead of being reused or recycled, there is a missed opportunity for businesses to generate revenue through resale or repurposing of these materials.
- Increased Production Costs: As the demand for textiles continues to rise, the production costs of raw materials, such as cotton and polyester, are also increasing. By reducing textile waste and promoting recycling, we can help alleviate the cost pressures on manufacturers.
- Disposal Expenses: Properly disposing of textile waste can be expensive for municipalities and waste management companies. These costs ultimately get passed on to taxpayers and consumers.
In order to mitigate the economic costs of textile waste, it is essential to encourage circular economy models, where textiles are reused, repaired, or recycled instead of being discarded.

Credit: www.sciencedirect.com
Mechanical Recycling
Mechanical recycling is a widely adopted method for textile waste recycling. This process involves converting used textiles into new fibers through various techniques. One of the primary approaches of mechanical recycling is fiber-to-fiber recycling, where existing textile materials are transformed into new fibers for textile production. There are two common techniques employed in mechanical recycling: shredding and reprocessing.
Fiber-to-fiber Recycling
In fiber-to-fiber recycling, the aim is to extract the maximum possible value from textile waste by converting it into high-quality fibers that can be used to produce new textiles. This method focuses on preserving the inherent properties of the original fibers and ensuring minimal degradation during the recycling process.
Through advanced technology, textile waste is sorted according to fiber type, color, and other relevant characteristics. This segregation process ensures that different fibers do not get mixed, allowing for targeted recycling of specific textile materials. Sorting helps maintain the quality and strength of the recycled fibers, which is essential for producing durable and desirable end products.
Shredding And Reprocessing
Shredding is a crucial step in mechanical recycling. Large textile waste items are shredded into smaller pieces to facilitate further processing. Once shredded, these textile materials go through a refining process where any impurities and non-fiber components, such as buttons, zippers, or metal findings, are removed.
After the refining stage, the shredded textile waste is reprocessed into fiber form. This involves further mechanical processes, such as carding, combing, and blending to ensure the fibers have the necessary qualities for subsequent textile production. The reprocessed fibers are then spun into yarns or used in nonwoven applications to create new textile products.
Advantages Of Mechanical Recycling
Mechanical recycling offers several benefits that make it an attractive method for recycling textile waste:
- Reduces textile waste: Mechanical recycling prevents textile waste from ending up in landfills, reducing the environmental impact of the textile industry.
- Promotes resource conservation: By converting textile waste into new fibers, mechanical recycling helps conserve resources and reduce the need for virgin materials.
- Energy and cost-efficient: Manufacturing textiles from recycled fibers requires less energy and resources compared to producing textiles from scratch.
- Supports circular economy: Mechanical recycling contributes to the circular economy concept by reintroducing textile materials back into the production cycle.
Note: While mechanical recycling is effective in reducing textile waste, it is important to complement it with other recycling methods, such as chemical recycling and upcycling, to address the various challenges associated with textile waste.
Chemical Recycling
Chemical recycling is a process that utilizes various chemical reactions to transform textile waste into valuable materials. This method plays a significant role in minimizing textile waste and contributing towards a more sustainable future. Chemical recycling offers several techniques, including dissolving techniques and depolymerization methods, which help break down the textile waste into its constituent elements for further use.
Dissolving Techniques
Dissolving techniques involve the use of solvents to dissolve the textile waste, allowing for the separation of impurities and the recovery of valuable fibers. These techniques are especially effective for mixed textiles or materials that are difficult to recycle through conventional means. One commonly used dissolving technique is called solvent spinning.
This method employs a solvent that dissolves the textile waste, allowing for the recovery of filaments or fibers. The solvent is then separated from the dissolved waste, and the recovered fibers can be used to create new textile products.
Another dissolving technique known as ionic liquids is gaining popularity in chemical recycling processes. Ionic liquids are liquid salts with unique solvent properties that provide an alternative to traditional solvents. They offer several advantages, including lower environmental impact and the ability to work at lower temperatures.
Depolymerization Methods
Depolymerization is a process that involves breaking down the polymer chains of textile waste into smaller molecules. This method enables the recovery of monomers, which can be used to produce new polymers or synthetic materials. One depolymerization method commonly used in textile recycling is hydrolysis.
Hydrolysis involves the use of water or an aqueous solution to break down the polymer chains, resulting in the recovery of monomers. This method is particularly effective for polyester-based textiles, as it can separate the polyester fibers from other materials, such as cotton or elastane.
Another depolymerization method used in chemical recycling is called glycolysis. Glycolysis utilizes a glycol as a reagent to break down polyester fibers into monomers, which can then be used to create new polyester products.
| Dissolving Techniques | Depolymerization Methods |
|---|---|
| Solvent Spinning | Hydrolysis |
| Ionic Liquids | Glycolysis |
- Dissolving techniques utilize solvents for textile waste separation.
- Ionic liquids provide an alternative solvent option with lower environmental impact.
- Depolymerization methods break down polymer chains into monomers.
- Hydrolysis utilizes water to separate polyester fibers.
- Glycolysis uses glycol to break down polyester fibers.
Chemical recycling methods like dissolving techniques and depolymerization play a vital role in transforming textile waste into valuable resources. These advancements contribute to a more sustainable and eco-friendly textile industry, reducing waste and promoting a circular economy.

Credit: www.sciencedirect.com
Upcycling And Repurposing
Upcycling and repurposing are innovative methods used to transform textile waste into new products, extending their lifespan and reducing environmental impact. These techniques offer sustainable solutions that not only reduce textile waste but also promote creativity and resourcefulness. In this section, we will explore the creative techniques for textile upcycling and how textiles are repurposed in various industries.
Creative Techniques For Textile Upcycling
Textile upcycling is a process that involves transforming discarded textiles into higher-value products. This involves using creative techniques to give old textiles a new lease on life. Some of the popular creative techniques for textile upcycling include:
- Remnant Patchwork: This technique involves piecing together textile remnants or scraps to create unique patchwork designs. The diverse colors, patterns, and textures of the scraps add character and intrigue to the final product.
- Screen Printing: By applying new designs or patterns onto old textiles through screen printing, the fabric's appearance can be completely transformed. This technique allows for customization and personalization of upcycled textiles.
- Embroidery and Appliqué: Adding embroidery or appliqué designs to plain or worn-out textiles can enhance their visual appeal. This technique not only adds decorative elements but also reinforces the fabric, making it more durable.
Repurposing Textiles In Different Industries
Repurposing textiles involves utilizing discarded fabrics for alternative purposes in various industries. Some examples of repurposing textiles in different industries include:
| Industry | Repurposing Method |
|---|---|
| Fashion | Transforming outdated garments into trendy accessories or altering the fabric to create new clothing items. |
| Home Decor | Using old textiles to create cushion covers, quilts, or repurposing them as curtains or upholstery. |
| Automotive | Utilizing discarded textiles for insulation, soundproofing, or upholstery in vehicle interiors. |
| Construction | Using textile waste as insulation material or converting them into building materials such as soundproof panels or thermal drapes. |
By repurposing textiles in various industries, we can minimize waste generation and create a more sustainable future. These alternative uses not only reduce dependence on new materials but also provide unique and eco-friendly solutions.
Textile Waste Management Initiatives
Textile waste recycling methods play a crucial role in reducing the environmental footprint of the fashion industry. With increasing awareness about sustainability and the need for circular economies, various initiatives have been taken to manage textile waste effectively. This article explores two key aspects of textile waste management initiatives: industry collaborations and partnerships, and government regulations and policies.
Industry Collaborations And Partnerships
Collaborations and partnerships within the textile industry are crucial for an effective waste management system. Through these collaborations, different stakeholders, including fashion brands, textile manufacturers, and recycling facilities, can work together towards a common goal of minimizing textile waste. By sharing resources, knowledge, and expertise, these partnerships can drive innovation and develop sustainable solutions for textile waste recycling.
Some textile waste management initiatives have resulted in the formation of industry-led organizations and frameworks. For instance, the Sustainable Apparel Coalition (SAC) brings together major brands, retailers, and suppliers to improve the environmental and social performance of their products, including waste management. By establishing common standards and best practices, the SAC encourages collaboration between industry players, ensuring efficient waste management throughout the supply chain.
Government Regulations And Policies
Government regulations and policies play a pivotal role in shaping textile waste management practices. These regulations provide a framework for textile recycling and impose responsibilities on manufacturers and consumers. By implementing policies that promote sustainable practices and impose penalties for improper waste disposal, governments can create a supportive environment for textile waste management initiatives.
One example of government intervention is the Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) policy. Under this policy, textile manufacturers are held accountable for the end-of-life management of their products. By requiring manufacturers to develop recycling programs and encouraging the use of recycled materials, the EPR policy fosters a sustainable approach towards textile waste management.
Moreover, governments can also provide financial incentives or tax credits to businesses or organizations that adopt eco-friendly waste management practices. This encourages investment in technologies and facilities that support textile recycling, further strengthening the overall waste management system.
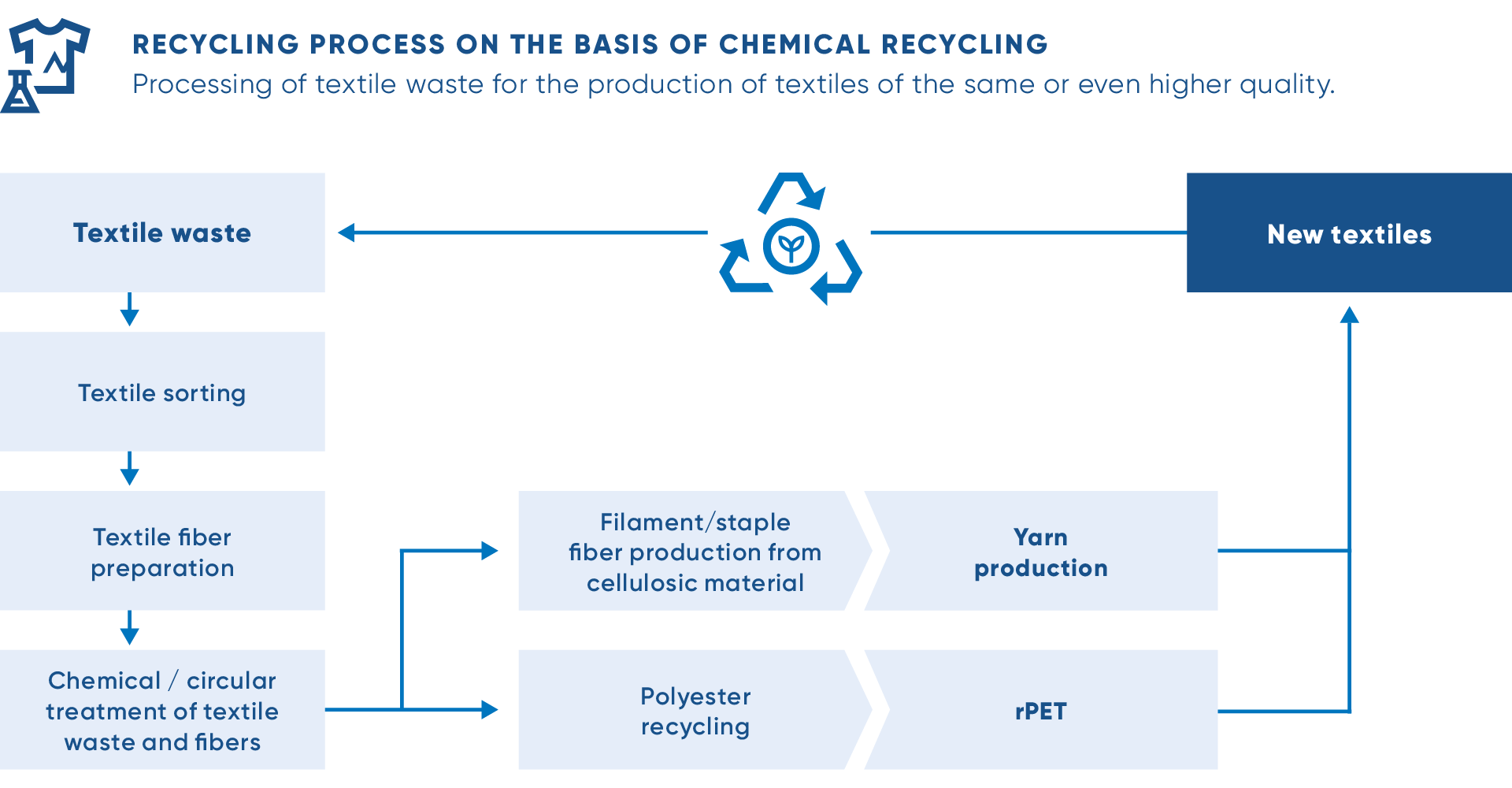
Credit: www.andritz.com
Frequently Asked Questions Of Textile Waste Recycling Methods
How Do You Recycle Textile Waste?
Textile waste can be recycled through various methods like mechanical recycling, chemical recycling, and upcycling. Mechanical recycling involves shredding and reprocessing textiles into new materials. Chemical recycling breaks down the fibers to produce new raw materials. Upcycling transforms waste fabrics into new products without breaking down the fibers.
What Are Some Examples Of Textile Recycling?
Some examples of textile recycling include donating used clothing to charities, repurposing old garments into new items, and recycling fabrics into materials for industrial use. It helps reduce waste and promote sustainability in the fashion industry.
What Are The Technologies For Textile Recycling?
Textile recycling utilizes several technologies, such as mechanical recycling, chemical recycling, and energy recovery. Mechanical recycling processes sort and break down fabrics, while chemical recycling involves converting them into fibers or raw materials. Energy recovery methods include incineration to generate electricity.
What Are Some Ways To Handle Textile Waste?
Some ways to handle textile waste include recycling, donating to thrift stores or charities, upcycling, and composting natural fibers.
Conclusion
Textile waste recycling methods play a pivotal role in achieving a sustainable future. By diverting textile waste from landfills, we can reduce environmental impact and promote a circular economy. From mechanical recycling to chemical processes, various techniques exist to transform textile waste into valuable resources.
By raising awareness and supporting these methods, we can contribute to a greener and more eco-friendly planet. Join the movement and be part of the solution!
Comments
Post a Comment